Sustainable Building Design
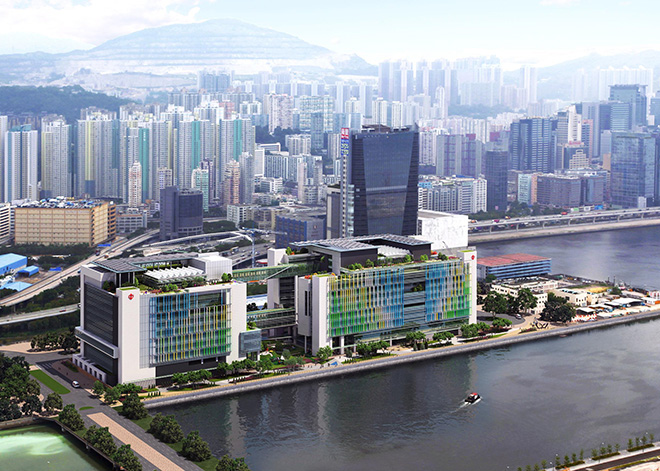
In Hong Kong, buildings account for over 90% and 60% of the citywide electricity consumption and carbon emissions respectively. Over the years, we are fully committed to adopting innovative sustainable and smart building design to enhance the efficient use of energy, material and land resources.
Passive Design Approach
Passive design approach uses building architecture to minimise energy consumption and improve thermal comfort. Suitable measures in planning, disposition, orientation, building form and material selection are adopted to optimise interaction with the local microclimate. Our considerations aspects include:
Mitigating heat island effect or elevated temperature

Air ventilation around buildings
Daylighting
Natural ventilation
Passive cooling

Reducing heat gain through building envelope
Active Design Approach
Active design approach uses electrical and mechanical systems to create and maintain comfortable conditions. These installations will facilitate energy efficiency, conservation of water, and improve indoor environmental quality. Our considerations aspects include:
Heating, water efficient devices, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems
Lighting systems
Renewable energy technologies
Selection of Construction Methods and Materials
The selection of sustainable construction methods and materials is another important aspect of sustainable buildings. Common practices include prefabrication, pollution control during construction and the application of reduce, reuse and recycle (3R) principles to manage construction and demolition waste. In terms of sustainable materials, recycled materials and timber from well-managed sources are widely adopted in ArchSD’s new building projects.
Social Considerations
The accessibility and quality of public spaces is highly valued in Hong Kong as a cosmopolitan city. We strive to incorporate social considerations in many of our buildings by enabling group activities and communication of community members, in order to create a harmonious atmosphere within the city.
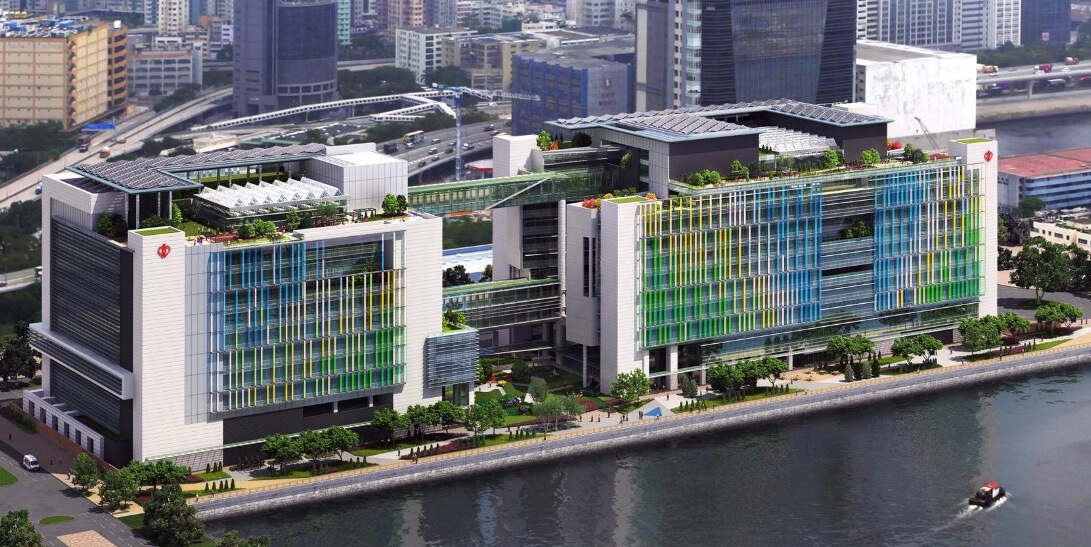

- Automatic demand control of chilled water circulation system
- Automatic demand control of fresh air supply with carbon dioxide sensors
- Heat wheel for heat energy reclaim of exhaust air
- Heat pump for hot water / space heating / dehumidification
- Solar hot water and photovoltaic panels on roof top
- Rainwater and condensate water recycling systems
- Over 40% of greenery coverage on ground floor, terraces and vertical greening on fences to reduce the heat island effect and improve air quality
- Maximisation of building perimeter and provision of atrium to maximise daylight penetration
- Vertical shading on the building façade to reduce glare and heat to achieve substantial energy savings and thermal comfort.
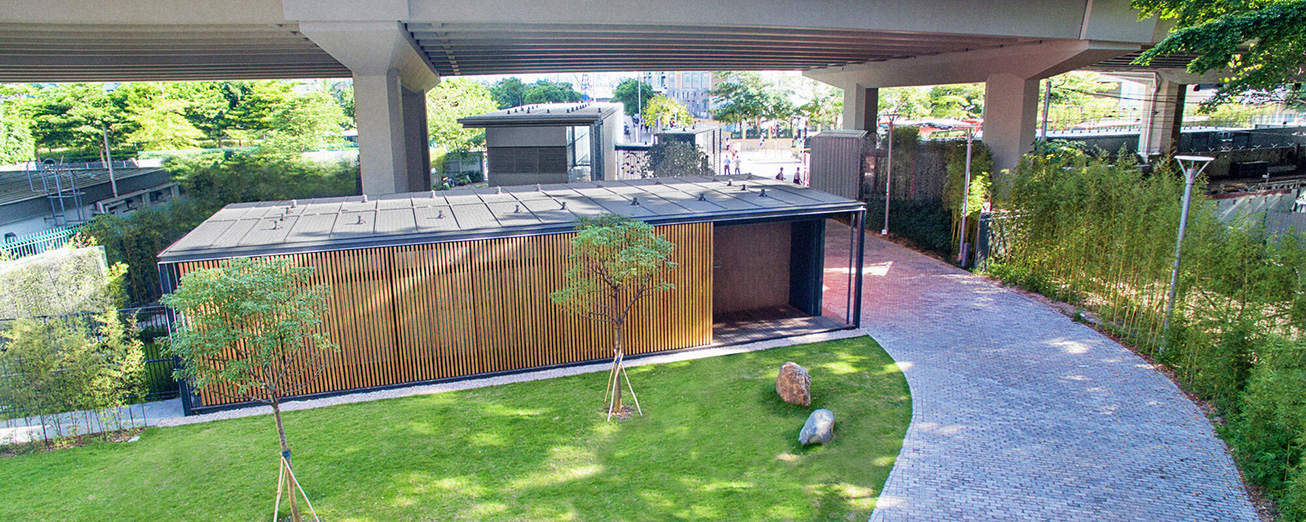

- Adoption of large overhanging roof and vertical greening to reduce solar heat gain thus reduce energy consumption significantly
- Implementation of various greening features such as green wall and courtyard garden
- Application of low-E glazing on windows to use natural daylight yet minimise heat gain to increase energy efficiency
- The flyover above HKECGS contributes to the passive cooling of the building.
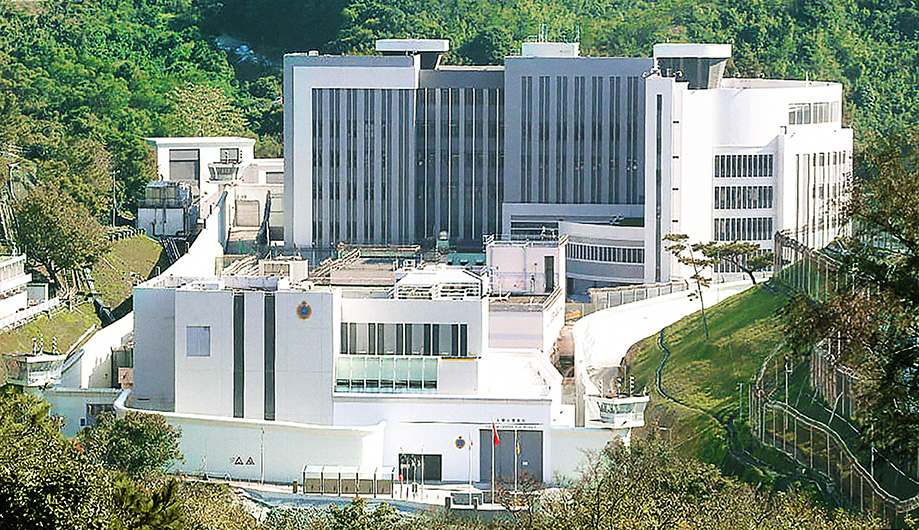

- Variable refrigerant volume (VRV) air-conditioning system
- T5 energy efficiency fluorescent tubes with electronic ballast and lighting control by occupancy sensors
- Light-emitting diode (LED) type exit signs
- Heat pump for domestic hot water
- Automatic on/off switching of lighting and ventilation fan inside the lift
- Renewable energy systems such as a solar hot water system and a photovoltaic system
- Greening features on rooftops
- Rainwater recycling system for landscape irrigation.