Energy Efficiency & Conservation - Building Orientation, Building Envelop & Sun-shading Devices
Energy efficiency & conservation means to reduce energy used in the construction process including the extraction, processing and transportation of construction materials, and the operation of the buildings. Since building use accounts for about 89% of electricity consumption in Hong Kong, reducing the amount of energy consumed for the operation of buildings is essential. Therefore when designing a sustainable building, we should encourage the design of structural elements, choice of materials and operating systems that result in more energy efficiency and conservation in the lifetime of the building.
Please click here to access more information on Energy Efficiency and Conservation.
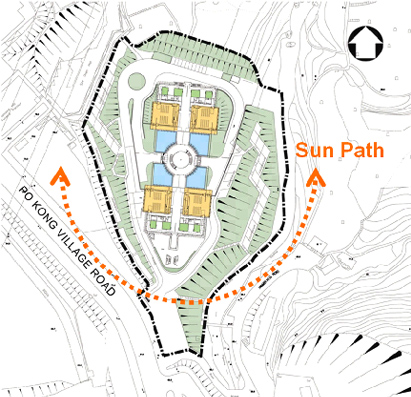
Building Orientation
Building orientation is the positioning of a building on the site. It is often considered to optimize the sun’s capacity for daylight and heat gain in winter. Different aspects of a building do not have equal access to the sun. Therefore each orientation should be treated differently to optimize the result. For example, windows facing north and south generally have good access to daylight and should be encouraged whilst windows facing west generally have excessive solar heat gain and therefore should be minimized.
Buildings with good natural light penetration will save considerable energy costs during the daytime. The glass walls of the library and conference room at the Stanley Complex are examples of daylight penetration. Occupancy sensors for control of office lights can avoid unnecessary lighting when a room is not in use. Other considerations of visual access include minimization of light pollution and maintaining visual privacy from exterior.
Building Envelop & Sun-shading devices
Building envelop provides separation of the interior and the exterior environment of a building. It serves as the outer shell to protect the indoor environment such as stopping the ingress of contaminated air and moisture as well as to facilitate its thermal control to achieve high level performance on energy efficiency. The following are some major considerations when designing the building envelop:
Structural integrity
Nature Lighting
Moisture control
Temperature Control
Sun shading is an essential element to consider during sustainable building design because of the following reasons:
Reduce heat gain
Reduce glare
Improve lighting quality
Provide privacy
UV protection
Save energy



















_EN_85x50.png)